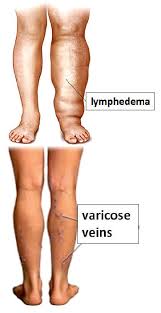
Venous insufficiency and lymphedema are two common but often misunderstood conditions that affect the body’s ability to manage fluid balance, particularly in the legs. While they are distinct medical issues, they can be interconnected, with venous insufficiency sometimes leading to or exacerbating lymphedema
Venous insufficiency occurs when the veins in the legs are unable to efficiently return blood to the heart, resulting in backward flow and pooling of blood in the legs.. This condition can lead to swelling, pain, and varicose veins, as well as more serious complications like venous ulcers.
Lymphedema is a condition caused by a blockage in the lymphatic system, leading to the build-up of lymph fluid in the tissues, affecting the arms or legs and results in swelling, discomfort, and skin changes. One of the key triggers for secondary lymphedema is venous insufficiency
How Venous Insufficiency Leads to Lymphedema
When venous insufficiency persists, it creates a chronic state of increased pressure within the veins of the legs causing blood and fluid to leak into the surrounding tissues. The lymphatic system becomes overwhelmed by this extra fluid load. Over time, if the lymphatic system can no longer keep up with the increased fluid volume, lymphedema develops, thereby leading to long-term damage.
The accumulation of fluid and protein-rich lymph in the tissues creates an environment ripe for inflammation. Chronic inflammation can damage both the veins and lymphatic vessels, leading to worsening of venous insufficiency and further progression of lymphedema.
How Venous Insufficiency Leads to Lymphedema
- ● Swelling
- ● Heaviness of the limb and Fatigue
- ● Tight, Thickened Skin
- ● Recurrent Infections
- ● Venous Ulcers
Venous Insufficiency and Lymphedema can be diagnosed with Doppler ultrasound, Lymphoscintography and Physical examination.
Treatment Options often requires a combination of therapies aimed at improving circulation, reducing swelling, and preventing complications. Key treatment strategies include:
- 1. Compression Therapy
- 2. Exercise and Elevation
- 3. Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
- 4. Venous Insufficiency Procedures like vein stripping or ligation
- 5. Skin Care / Hygiene
- 6. Medications
Conclusion
Venous insufficiency can set off a chain reaction in the body, leading to complications like lymphedema. When the veins are unable to efficiently return blood to the heart, the resulting build-up of fluid places extra stress on the lymphatic system which causes the lymphatic system to fail, resulting in chronic swelling, tissue damage, and other complications.
Early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan can help manage both venous insufficiency and lymphedema, preventing further progression and improving quality of life.
