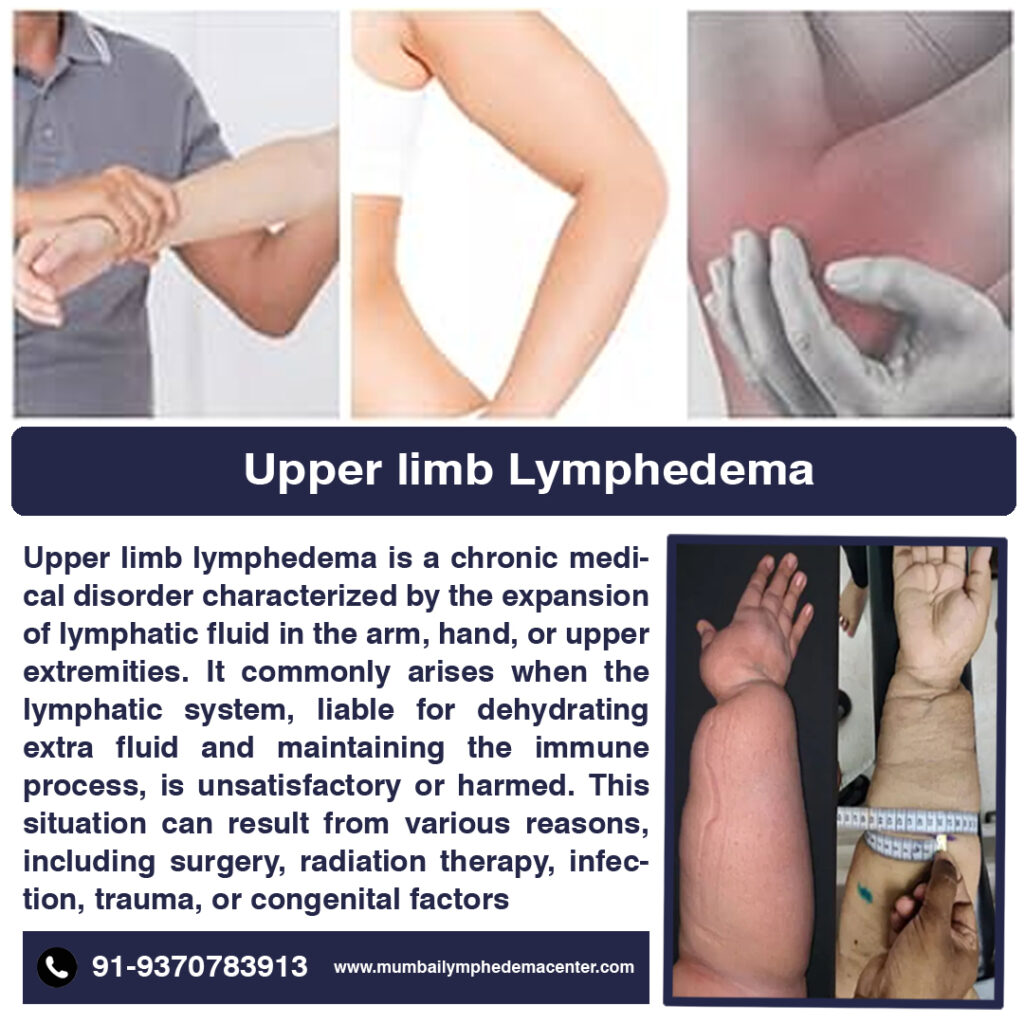
Upper limb lymphedema is a chronic medical disorder characterized by the expansion of lymphatic fluid in the arm, hand, or upper extremities. It commonly arises when the lymphatic system, liable for dehydrating extra fluid and maintaining the immune process, is unsatisfactory or harmed. This situation can result from various reasons, including surgery, radiation therapy, infection, trauma, or congenital factors. Upper limb lymphedema can lead to swelling, discomfort, reduced mobility, and an increased risk of infections. Management strategies include compression therapy, exercise, skincare, and sometimes surgical interventions.
In this summary, we will talk about upper limb lymphedema :
- 1. Definition: Upper limb lymphedema is a situation where there is swelling and fluid retention in the arms and hands due to impaired lymphatic drainage.
- 2. Causes: Common Uses include surgical disposal of lymph nodes, radiation treatment, infections (e.g., cellulitis), and hereditary aspects. Cancer treatments, especially for breast cancer, are a significant trigger.
- 3. Symptoms: Patients constantly experience swelling, discomfort, heaviness, and a lower range of gestures in the affected limb. Skin modifications, such as thickening or hardening, can also happen.
- 4. Diagnosis: Doctors diagnose upper limb lymphedema through clinical evaluation, medical history, and imaging examinations like lymphoscintigraphy.
- 5. Management: Management strategies focus on decreasing swelling and enhancing quality of life. This includes:
- ● Compression Therapy: Wearing compression habiliment to help lymphatic discharge
- ● Physical Therapy: Exercises and manual lymphatic drainage techniques to facilitate circulation.
- ● Medications: Some medications may be specified to organize signs and decrease inflammation.
- 6. Surgery: Surgical interventions like Lymphovenous Bypass and Vascularized Lymph node transfer can be planned in collaboration with conservative methods to prevent further progression and yield a better quality of life.
- 7. Lifestyle Modifications: Patients are encouraged to retain a healthy weight, bypass injury, and practice good skin care to prevent disease.
- 8. Complications: If left untreated, upper limb lymphedema can lead to recurrent diseases, reduced limb procedures, and a lower quality of life.
- 9. Prevention: Reducing the risk of upper limb lymphedema implicates reasonable post-surgical care, before the distinction of signs, and diligent administration.
- 10. Support: Patients are frequently satisfied with support groups and counseling to manage the expressive and psychological characteristics of residents with lymphedema.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.