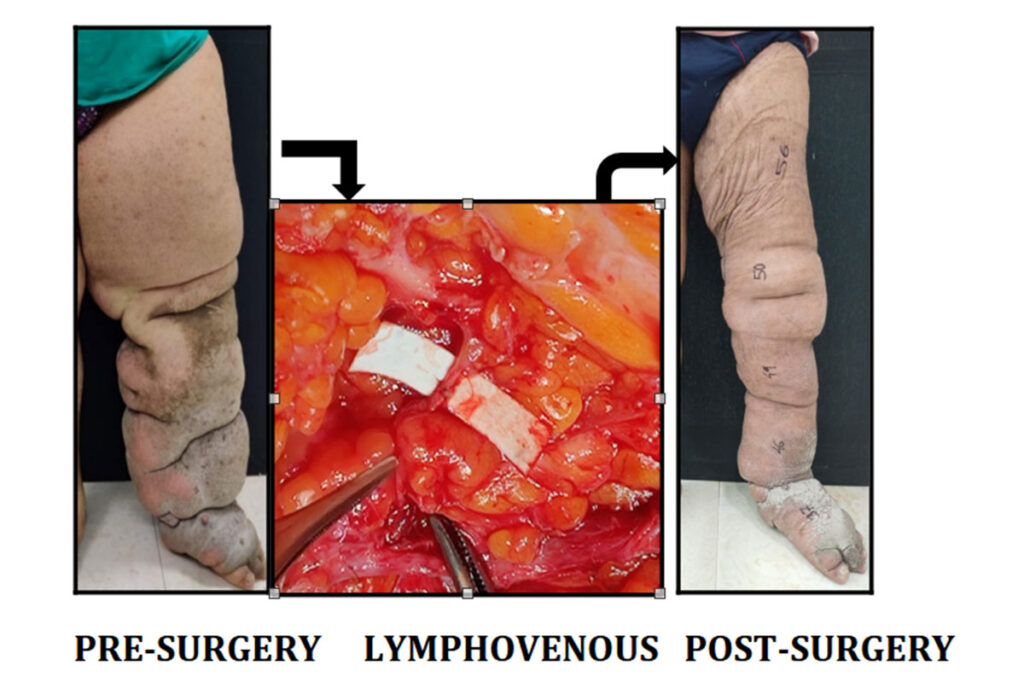
PRE-SURGERY
LYMPHOVENOUS
POST-SURGERY
BYPASS
Filariasis / Elephantiasis is a parasitic disease, primarily leading to swelling in the lower limbs, caused by filarial worm infections, Wuchereria bancrofti, that are transmitted by mosquito bites. This obstruction impairs lymphatic drainage, leading to lymphedema, a condition where lymphatic fluid accumulates in the tissues, causing chronic swelling and inflammation. This disease can result in decreased work productivity, disability, and social stigma.
What is a Lymphaticovenous Bypass?
Lymphaticovenous bypass is a microsurgical procedure in which the surgeon identifies and isolates the lymphatic vessels using specialized microscopes. Tiny incisions are made, blocked lymphatic vessels are connected to nearby small veins/ venules of similar calibre, allowing excess lymph fluid to drain into the venous system, where it can be processed and eliminated from the body.
Post-surgery, patients usually experience a gradual reduction in limb swelling, with significant improvement often seen within months.
Conservative treatments like compression therapy, skincare, and exercise can help manage symptoms, but in advanced stages, these may not be enough to provide long-term relief.
Lymphaticovenous bypass offers several advantages for eligible patients:
- ● Minimal Invasiveness: This microsurgical technique involves small incisions and is less invasive compared to other surgical interventions.
- ● Long-term Relief: By directly addressing the lymphatic obstruction, LVB can provide more sustained relief from swelling than non-surgical treatments.
- ● Improved Quality of Life: Restoring lymphatic function can improve mobility, reduce discomfort, and improve cosmetic outcomes, thus significantly enhancing daily life.
Post-Surgical Care
Following the surgery, patients may need to continue compression therapy and physical therapy to maintain lymphatic drainage. Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor progress and ensure that the bypass remains effective.
Conclusion
For patients suffering from lower limb filariasis-induced lymphedema, lymphaticovenous bypass presents a promising solution. This microsurgical procedure offers hope for long-term relief and a better quality of life by addressing the root cause of lymphedema.